Knee pain is a common complaint for which they seek medical attention. What causes the pain and how to help yourself if it happens? There is no definite answer, because the knee joint can suffer all kinds of damage arising from many causes. One of these (and very common) reasons is early-stage arthritis. Today we will tell you in detail about knee effusion: its causes, types, symptoms and signs, we will talk about methods of treatment and prevention.
Types and causes of diseases
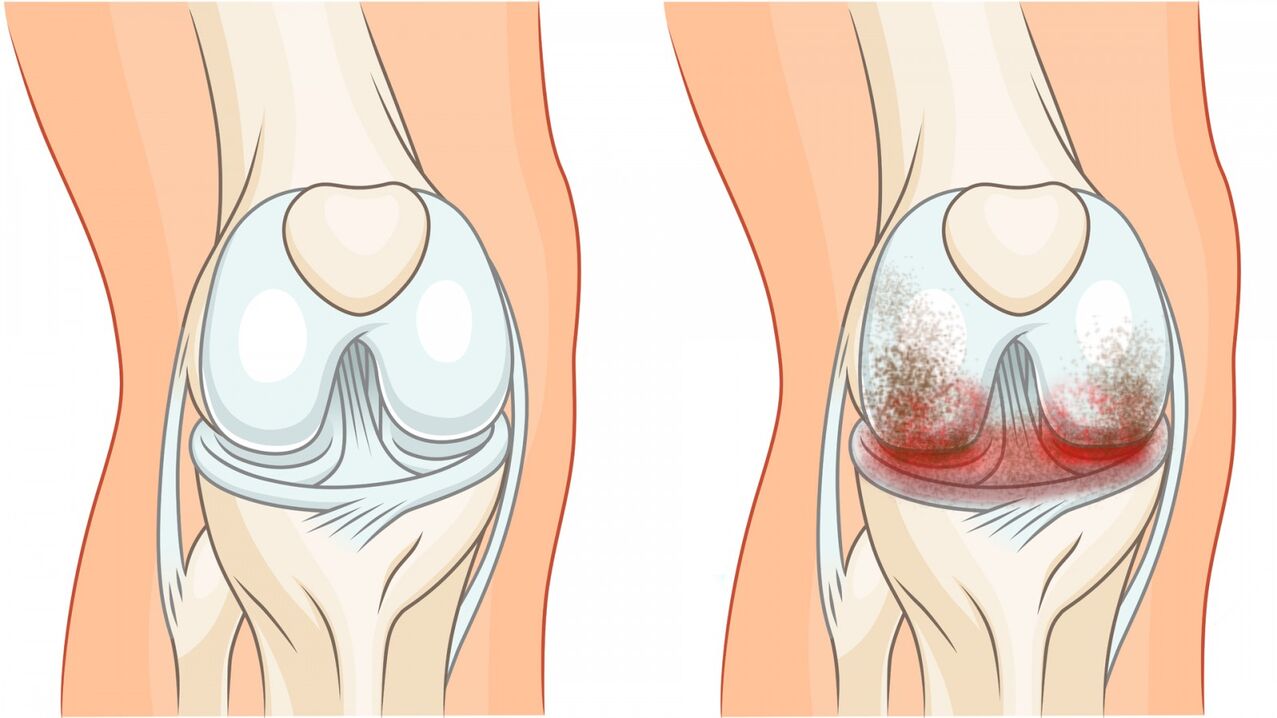
Knee osteoarthritis or gonarthrosis is a predominantly non-inflammatory injury that eventually leads to cartilage destruction, deformity of the knee joint, and limited range of motion of the knee joint. The disease has two main forms:
- primary - arising from a congenital joint defect;
- secondary - arises as a result of other diseases or injuries.
The primary form begins to develop in childhood or youth and is caused by improper formation of the joint surface or ligamentous apparatus. When walking, such a joint is subjected to loads disproportionate to its capacity, which causes degenerative changes in it.
The development of a secondary form of pathology can lead to:
- Trauma: leg fractures, bruises and dislocations of the knee, accompanied by damage to the bony and cartilaginous parts of the joint and the ligamentous apparatus of the joint. In this case, post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the knee joint will develop.
- Operations to remove the meniscus, as they lead to a violation of the integral structure of the knee and its rapid wear.
- The disproportionately high load on the legs is often subjected to athletes.
- Excessive obesity also causes arthritis, as it leads to excessive pressure from the body's weight on the articular cartilage of the knee.
- Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints. Chronic arthritis is accompanied by fluid build-up in the joint cavity and over time can lead to joint complications.
- Metabolic disorders lead to salt deposition in the joint cavities.
- Other factors and diseases associated with long-term spasm of the leg muscles or blood vessels.
- The transactions have been transferred.
The pathological process can be one- or two-sided. As a result of trauma, it is more likely to develop unilateral arthropathy (eg, in the right knee) and due to obesity - bilateral.

Typical symptoms
Osteoarthritis of the knee develops gradually, sometimes months or years ahead of its baseline, when there are no obvious symptoms (such as severe pain and visible deformity), but occasionallyfeeling uncomfortable inside. knee.
Often, women over 40 who are overweight suffer from the disease, and especially, as an exacerbating factor, varicose veins.
The development of gonarthrosis goes through several stages:
- The initial phase can last for months and sometimes years. A person is concerned about cyclical pain in the knee, especially when taking the first steps after getting out of bed in the morning, as well as when going up and down stairs.
- In the second stage, the pain becomes stronger and occurs with any movement accompanied by a characteristic crunching sound. There can be fluid accumulation in the joint cavity and upon examination you may notice the initial deformity. Range of motion in the affected knee begins to decrease.
- The third stage is characterized by pain that does not go away even with rest. The discomfort is usually worse before the weather changes. By this time, the joints have almost lost their function: the leg may be nearly unkempt or not fully flexed. Altered gait: becoming "waddling" or bent legs. The deformity of the knee is very pronounced: the leg is bent and has an O or X shape.
Symptoms of post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the knee joint develop more rapidly. Against the background of injury, pain appears in the knee area and swelling. Such pain constantly accompanies a person and increases after physical exertion. Gradually, the feeling of tension and stiffness in the knee joined it. Sometimes, with this form of the disease, it takes only a few months to go from the initial symptoms to irreversible changes.
Treatment of gonarthrosis
The extent of treatment depends on the stage of the disease and the severity of the lesion. But since the disease is chronic, the only thing that can be achieved is long-term remission (a period of rest when manifestations of the disease are few or none). At the same time, if the cause of the knee dryness can be eliminated in the early stages (eg, by reducing body weight), almost complete recovery is possible.
Goals of treatment for gonarthrosis:
- remove pain,
- if possible, restore the damaged cartilaginous and ligamentous apparatus,
- increase range of motion in the joint.
Treatments:
- drug treatment,
- massage and manual therapy,
- surgical intervention,
- rehabilitation therapy (exercise therapy, physical therapy and others).
Only a doctor can choose the right drug - in no case should it not be self-prescribed. Their main action is to:
- Eliminates the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee: relieves pain and inflammation. For this, appropriate drugs are prescribed, including hormones, which are injected into the joint cavity.
- Improves blood supply to the affected area. It is provided by reducing blood vessel spasms and relaxing muscles.
- Cartilage restoration. For this, drugs are prescribed to nourish and restore cartilage.
Hand massage and impact relieve pain, relax tight muscles near the affected knee, increase range of motion, correct bone position, increase blood circulation.
With deep, irreversible damage, knee effusion is treated with a radical method - prosthetics, i. e. , implanting a metal prosthesis to replace the destroyed joint. So far, this is the only way that offers a chance of full recovery, however, endoprosthes have a limited lifespan, after which they must be replaced. Since the cost of such operations is very high, this method of treatment has not yet gained popularity.
Rehabilitation therapy includes physical therapy, kinesitherapy (exercises using special loads and simulators), physiotherapy and spa treatments.
Orthopedic methods aimed at eliminating painful knees - these are canes, orthotics, etc. v. , facilitate travel (use if necessary).
There are many folk recipes for different ointments and compresses based on herbs, medical honey and warm bandages made from natural wool used. Basically, the action of such methods is aimed at reducing pain and eliminating the main symptoms.
Preventive measures
Prevention of knee disease involves many factors:
- Balanced diet: The diet should have adequate amounts of protein, vitamins and minerals.
- Fight against wrong lifestyle and get rid of bad habits.
- Normalize weight.
- Full physical activity.
- Preventing injuries when playing sports, lifting weights.
The most important thing in determining a pathology such as osteoarthritis of the knee is not the onset of the disease, since its stages of development lead to disability. But if every effort is directed at timely treatment and prevention - until the time is gone and the symptoms are insignificant - there is still a chance of a complete cure of the disease.

























